workqueue提供了一个简单的队列,支持以下功能:
- 按添加顺序处理item。
- 单个item不会同时被处理多次,如果一个项目在被处理前被添加了多次,它只会被处理一次。
- 允许一个item在处理过程中被重新排队。
WorkQueue
版本: kubernetes-v1.20.11内置client-go: staging/src/k8s.io/client-go
普通队列
定义位于util/workqueue/queue.go:26
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| type Interface interface {
Add(item interface{})
Len() int
Get() (item interface{}, shutdown bool)
Done(item interface{})
ShutDown()
ShuttingDown() bool
}
|
Type结构体默认实现了该接口。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| type Type struct {
// queue defines the order in which we will work on items. Every
// element of queue should be in the dirty set and not in the
// processing set.
queue []t
// dirty defines all of the items that need to be processed.
dirty set
// Things that are currently being processed are in the processing set.
// These things may be simultaneously in the dirty set. When we finish
// processing something and remove it from this set, we'll check if
// it's in the dirty set, and if so, add it to the queue.
processing set
...
}
|
主要字段:
- queue:类型为
[]interface{},定义了处理所有元素的顺序。queue中的每个元素都应该在dirty集中而不是在processing集中 - dirty:类型为set,即map[string]struct{}。存储了所有需要处理的元素并保证了没有重复。
- processing:类型为set。存储了当前正在被处理的元素,这些元素可能也在
dirty中,当处理完某个item后,从processing中删除该数据并且检查是否在dirty中,如果是则重新加入到queue中
看下Type结构体实现Interface的具体方法,重点看Add/Get/Done
Add() – 向队列添加元素
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
| func (q *Type) Add(item interface{}) {
q.cond.L.Lock()
defer q.cond.L.Unlock()
if q.shuttingDown { // 检查是否正在关闭,是则直接返回
return
}
if q.dirty.has(item) { // dirty中已有该字段,直接返回。保证queue中没有重复数据
return
}
q.metrics.add(item)
q.dirty.insert(item) // 向dirty中添加该item
if q.processing.has(item) { // 若procssing存在该字段,直接返回。该item正在被处理则直接返回
return
}
q.queue = append(q.queue, item) // 将item添加到queue中
q.cond.Signal()
}
|
添加元素时会同时向dirty和queue中添加;如果向dirty中添加后发现processing中也有该元素则不向queue中添加
Get() – 从队列获取元素
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
| func (q *Type) Get() (item interface{}, shutdown bool) {
q.cond.L.Lock()
defer q.cond.L.Unlock()
for len(q.queue) == 0 && !q.shuttingDown { // queue为空但是不是正在关闭,阻塞等待
q.cond.Wait()
}
if len(q.queue) == 0 {
// We must be shutting down.
return nil, true
}
item, q.queue = q.queue[0], q.queue[1:] // 从queue中取出第一个元素
q.metrics.get(item)
q.processing.insert(item) // 向processing添加该元素
q.dirty.delete(item) // 从dirty中删除该元素
return item, false
}
|
获取元素时会从queue中获取第一个元素,添加到processing中,并且从dirty中删除。
Done() – 标记某个元素已处理完
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| func (q *Type) Done(item interface{}) {
q.cond.L.Lock()
defer q.cond.L.Unlock()
q.metrics.done(item)
q.processing.delete(item) // 从processing中删除该元素
if q.dirty.has(item) { // 如果dirty中仍然存在该元素,重新加入到queue中
q.queue = append(q.queue, item)
q.cond.Signal()
}
}
|
删除元素时从processing中删除,如果dirty依然存在则重新加入到queue中
综上:queue是实际存储元素的位置,dirty在保证去重的同时可以保证即使一个元素被添加多次也仅会处理一次,processing用于某个元素正在被处理。


延迟队列
延迟队列的定义位于:util/workqueue/delaying_queue.go:30,主要在普通队列的基础上添加了AddAfter方法,主要原理是在等待duration时间后添加到队列中。
1
2
3
4
5
| type DelayingInterface interface {
Interface
// AddAfter adds an item to the workqueue after the indicated duration has passed
AddAfter(item interface{}, duration time.Duration)
}
|
默认实现的结构体为delayingType
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
| type delayingType struct {
Interface
// clock tracks time for delayed firing
clock clock.Clock
// stopCh lets us signal a shutdown to the waiting loop
stopCh chan struct{}
// stopOnce guarantees we only signal shutdown a single time
stopOnce sync.Once
// heartbeat ensures we wait no more than maxWait before firing
heartbeat clock.Ticker
// waitingForAddCh is a buffered channel that feeds waitingForAdd
waitingForAddCh chan *waitFor // 主要字段,包含要添加的元素及添加时间。默认为1000
// metrics counts the number of retries
metrics retryMetrics
}
|
AddAfter() – 等待一段时间添加到队列
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
| func (q *delayingType) AddAfter(item interface{}, duration time.Duration) {
// don't add if we're already shutting down
if q.ShuttingDown() { // 队列正在关闭,直接返回
return
}
q.metrics.retry()
// immediately add things with no delay
if duration <= 0 { // 如果duration小于0立即添加
q.Add(item)
return
}
select {
case <-q.stopCh:
// unblock if ShutDown() is called
case q.waitingForAddCh <- &waitFor{data: item, readyAt: q.clock.Now().Add(duration)}:
// 向waitForAddCh添加元素
}
}
|
在delayingType的构造方法中,由goroutine中运行的waitingLoop持续处理由AddAfter()方法添加进来的item
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| func newDelayingQueue(clock clock.Clock, q Interface, name string) *delayingType {
ret := &delayingType{
Interface: q,
clock: clock,
heartbeat: clock.NewTicker(maxWait),
stopCh: make(chan struct{}),
waitingForAddCh: make(chan *waitFor, 1000), // waitingForAddCh默认长度为1000
metrics: newRetryMetrics(name),
}
go ret.waitingLoop()
return ret
}
|
waitLoop() – 处理由AddAfter()添加进来的条目
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
| func (q *delayingType) waitingLoop() {
defer utilruntime.HandleCrash()
// Make a placeholder channel to use when there are no items in our list
never := make(<-chan time.Time)
// Make a timer that expires when the item at the head of the waiting queue is ready
var nextReadyAtTimer clock.Timer
waitingForQueue := &waitForPriorityQueue{}
heap.Init(waitingForQueue) // 初始化堆
waitingEntryByData := map[t]*waitFor{} // 创建t到waitFor的映射
for {
if q.Interface.ShuttingDown() { // 如果队列关闭则直接退出
return
}
now := q.clock.Now() // 获取当前时间
// Add ready entries
for waitingForQueue.Len() > 0 { // waitingForQueue非空进入循环
entry := waitingForQueue.Peek().(*waitFor) // 从waitingForQueue取出一个*waitFor
if entry.readyAt.After(now) { // 该entry未ready,跳出循环
break
}
entry = heap.Pop(waitingForQueue).(*waitFor) // 该entry如果ready,则从heap堆中弹出并添加到队列
q.Add(entry.data)
delete(waitingEntryByData, entry.data) // 从waitingEntryByData中删除已添加的t
}
// Set up a wait for the first item's readyAt (if one exists)
nextReadyAt := never
if waitingForQueue.Len() > 0 {
if nextReadyAtTimer != nil {
nextReadyAtTimer.Stop()
}
entry := waitingForQueue.Peek().(*waitFor) // 如果waitingForQueue有数据,则从中取出一个*waitFor
nextReadyAtTimer = q.clock.NewTimer(entry.readyAt.Sub(now))
nextReadyAt = nextReadyAtTimer.C() // (*waitFor的ready时间-当前时间)作为下个就绪时间点
}
select {
case <-q.stopCh:
return
case <-q.heartbeat.C():
// continue the loop, which will add ready items
case <-nextReadyAt: // 到达下一个就绪点开始有项目ready
// continue the loop, which will add ready items
case waitEntry := <-q.waitingForAddCh: // 处理由AddAfter()添加进来的entry
if waitEntry.readyAt.After(q.clock.Now()) { // 该entry未ready,则加入到waitingForQueue优先级队列中
insert(waitingForQueue, waitingEntryByData, waitEntry)
} else {
q.Add(waitEntry.data) // 如果已ready则直接入列
}
drained := false
for !drained { // 通过一个for循环消费掉所有的entry
select {
case waitEntry := <-q.waitingForAddCh:
if waitEntry.readyAt.After(q.clock.Now()) {
insert(waitingForQueue, waitingEntryByData, waitEntry)
} else {
q.Add(waitEntry.data)
}
default:
drained = true // q.waitingForAddCh没有新数据则跳出循环
}
}
}
}
}
|
其中waitForPriorityQueue是waitFor指针类型的切片,并且实现了heap.Interface。堆是实现优先级队列的常用方法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| type waitForPriorityQueue []*waitFor
// Len() Less() Swap() Pop() Push()是实现heap.Interface的方法
func (waitForPriorityQueue).Len() int
func (waitForPriorityQueue).Less(i int, j int) bool
func (waitForPriorityQueue).Peek() interface{}
func (*waitForPriorityQueue).Pop() interface{}
func (*waitForPriorityQueue).Push(x interface{})
func (waitForPriorityQueue).Swap(i int, j int)
|
insert()
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| // insert adds the entry to the priority queue, or updates the readyAt if it already exists in the queue
func insert(q *waitForPriorityQueue, knownEntries map[t]*waitFor, entry *waitFor) {
// if the entry already exists, update the time only if it would cause the item to be queued sooner
existing, exists := knownEntries[entry.data]
if exists {
if existing.readyAt.After(entry.readyAt) {
existing.readyAt = entry.readyAt
heap.Fix(q, existing.index) // 重新建立堆排序
}
return
}
heap.Push(q, entry)
knownEntries[entry.data] = entry
}
|
insert函数主要是添加entry到q这个优先级队列中,如果该entry已在knownEntries存在,则更新ready时间。
限速队列
限速队列的定义位于:util/workqueue/rate_limiting_queue.go:20
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| type RateLimitingInterface interface {
DelayingInterface
// AddRateLimited adds an item to the workqueue after the rate limiter says it's ok
AddRateLimited(item interface{})
// Forget indicates that an item is finished being retried. Doesn't matter whether it's for perm failing
// or for success, we'll stop the rate limiter from tracking it. This only clears the `rateLimiter`, you
// still have to call `Done` on the queue.
Forget(item interface{})
// NumRequeues returns back how many times the item was requeued
NumRequeues(item interface{}) int
}
|
限速队列在延迟队列的基础上又添加了三个方法:
- AddRateLimited:限速器判断可以添加时添加元素时调用延迟队列的AddAfter()方法添加元素
- Forget:达到一定失败次数或者成功时告知限速器忽略该item,当时仍然需要调用普通队列的Done()方法标记该item已经处理完
- NumRequeues:返回该item重新入列的次数
默认实现的结构体为rateLimitingType,可以看到全部于限速器RateLimiter有关。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| type rateLimitingType struct {
DelayingInterface
rateLimiter RateLimiter
}
func (q *rateLimitingType) AddRateLimited(item interface{}) {
q.DelayingInterface.AddAfter(item, q.rateLimiter.When(item))
}
func (q *rateLimitingType) NumRequeues(item interface{}) int {
return q.rateLimiter.NumRequeues(item)
}
func (q *rateLimitingType) Forget(item interface{}) {
q.rateLimiter.Forget(item)
}
|
RateLimiter – 限速器定义
其中RateLimiter是限速器的接口定义,定义位于util/workqueue/default_rate_limiters.go:27
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| type RateLimiter interface {
// When gets an item and gets to decide how long that item should wait
When(item interface{}) time.Duration // 元素需要等待多长时间
// Forget indicates that an item is finished being retried. Doesn't matter whether its for perm failing
// or for success, we'll stop tracking it
Forget(item interface{}) // 告知限速器忘记元素
// NumRequeues returns back how many failures the item has had
NumRequeues(item interface{}) int // 元素重新入列的次数
}
|
rateLimitingType的大部分方法是直接与RateLimiter相关的。其中AddRateLimited直接调用了延迟队列中的AddAfter方法,入参是从RateLimiter的When方法返回的值。
client-go默认4种实现RateLimiter的算法:
- BucketRatelimiter:令牌桶限流算法
- ItemExponentialFailureRateLimiter:指数失败限流算法
- ItemFastSlowRateLimiter: 计数器快慢限流算法
- MaxOfRateLimiter:混合限流算法
BucketRatelimiter – 令牌桶算法

令牌桶算法在内部维护了一个存放token的桶,起初是满的,token会以r tokens/s的速度加入到bucket中,每个item从令牌桶中获取一个token,只有得到token才允许通过,否则等待若干时间。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
| import (
"golang.org/x/time/rate"
)
type BucketRateLimiter struct {
*rate.Limiter
}
var _ RateLimiter = &BucketRateLimiter{}
func (r *BucketRateLimiter) When(item interface{}) time.Duration {
return r.Limiter.Reserve().Delay()
}
func (r *BucketRateLimiter) NumRequeues(item interface{}) int {
return 0
}
func (r *BucketRateLimiter) Forget(item interface{}) {
}
|
令牌桶算法直接使用了golang.org/x/time/rate包作为实现。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| func DefaultControllerRateLimiter() RateLimiter {
return NewMaxOfRateLimiter(
NewItemExponentialFailureRateLimiter(5*time.Millisecond, 1000*time.Second),
// 10 qps, 100 bucket size. This is only for retry speed and its only the overall factor (not per item)
&BucketRateLimiter{Limiter: rate.NewLimiter(rate.Limit(10), 100)},
)
}
|
在DefaultControllerRateLimiter()中初始化BucketRateLimiter时调用了rate.NewLimiter(r,b)进行了初始化。
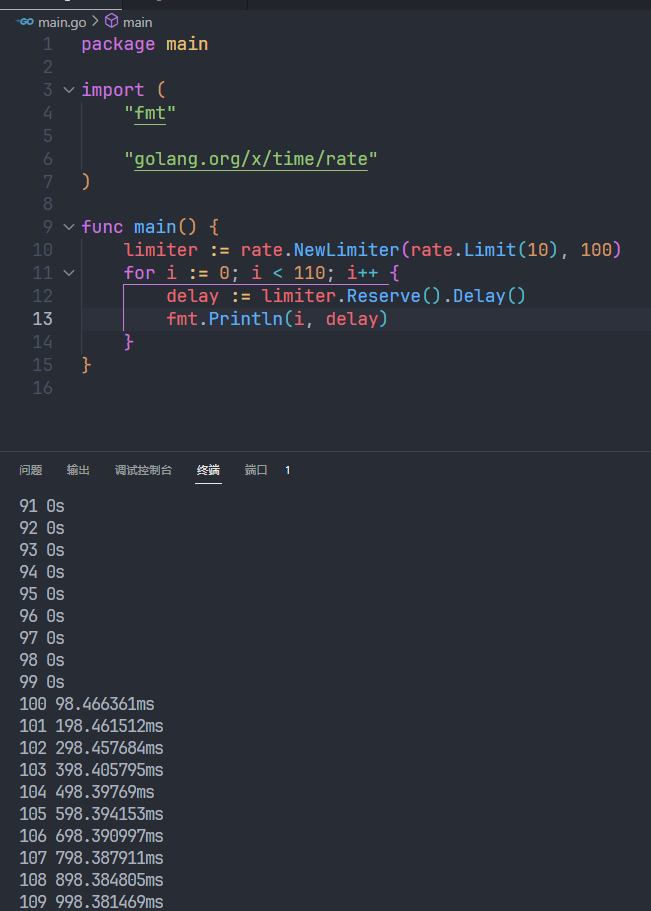
测试发现基于DefaultControllerRateLimiter()的配置参数中,前100个item直接入列没有延迟,后面的item每次增加延迟100ms,以此类推。
ItemExponentialFailureRateLimiter – 指数失败限速算法
在DefaultControllerRateLimiter()同样初始化了ItemExponentialFailureRateLimiter结构体
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| func DefaultControllerRateLimiter() RateLimiter {
return NewMaxOfRateLimiter(
NewItemExponentialFailureRateLimiter(5*time.Millisecond, 1000*time.Second),
// 10 qps, 100 bucket size. This is only for retry speed and its only the overall factor (not per item)
&BucketRateLimiter{Limiter: rate.NewLimiter(rate.Limit(10), 100)},
)
}
|
ItemExponentialFailureRateLimiter结构体及方法:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
| type ItemExponentialFailureRateLimiter struct {
failuresLock sync.Mutex
failures map[interface{}]int // item -> 次数的映射
baseDelay time.Duration // 基础时延
maxDelay time.Duration // 最大时延
}
func NewItemExponentialFailureRateLimiter(baseDelay time.Duration, maxDelay time.Duration) RateLimiter {
return &ItemExponentialFailureRateLimiter{
failures: map[interface{}]int{},
baseDelay: baseDelay,
maxDelay: maxDelay,
}
}
func DefaultItemBasedRateLimiter() RateLimiter { // 额外的初始化方法,DefaultControllerRateLimiter不使用
return NewItemExponentialFailureRateLimiter(time.Millisecond, 1000*time.Second)
}
func (r *ItemExponentialFailureRateLimiter) When(item interface{}) time.Duration {
r.failuresLock.Lock()
defer r.failuresLock.Unlock()
exp := r.failures[item]
r.failures[item] = r.failures[item] + 1
// The backoff is capped such that 'calculated' value never overflows.
backoff := float64(r.baseDelay.Nanoseconds()) * math.Pow(2, float64(exp)) // 指数退避计算延迟
if backoff > math.MaxInt64 { // 若超过Int64最大值返回最大时延
return r.maxDelay
}
calculated := time.Duration(backoff)
if calculated > r.maxDelay { // 如果指数退避的计算结果超过最大时延,返回最大时延
return r.maxDelay
}
return calculated
}
func (r *ItemExponentialFailureRateLimiter) NumRequeues(item interface{}) int {
r.failuresLock.Lock()
defer r.failuresLock.Unlock()
return r.failures[item]
}
func (r *ItemExponentialFailureRateLimiter) Forget(item interface{}) {
r.failuresLock.Lock()
defer r.failuresLock.Unlock()
delete(r.failures, item)
}
|
测试DefaultControllerRateLimiter中的初始化参数NewItemExponentialFailureRateLimiter(5*time.Millisecond, 1000*time.Second)
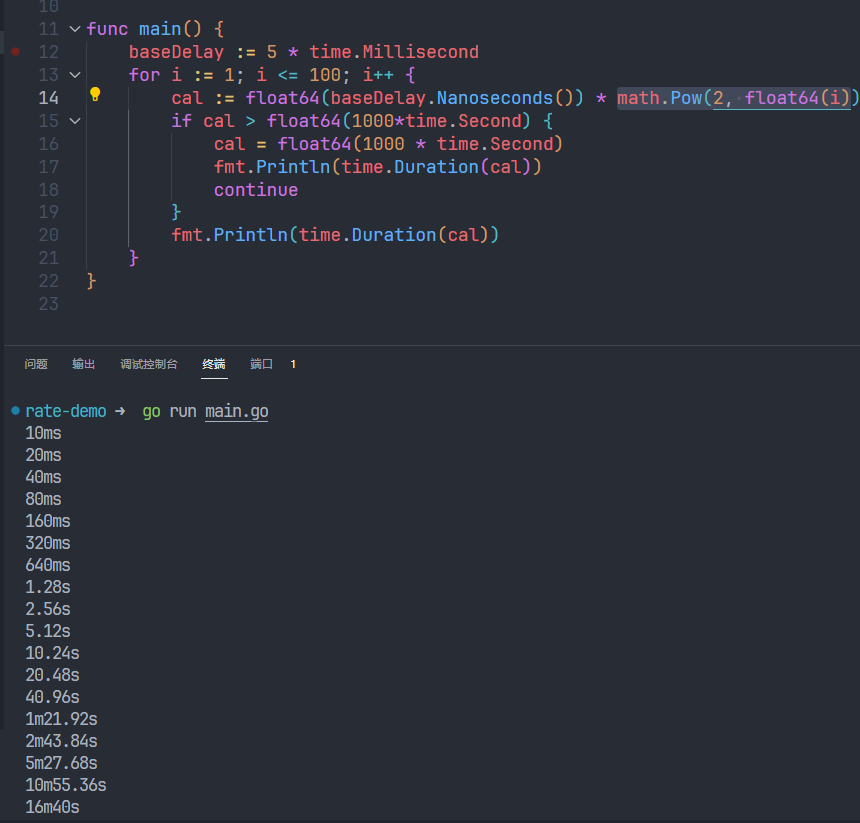
也就是每个item进来至少等待10ms,如果有重复的item按指数退避算法进行等待,最长时间为16m40s。
ItemFastSlowRateLimiter – 计数器快慢算法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
| type ItemFastSlowRateLimiter struct {
failuresLock sync.Mutex
failures map[interface{}]int
maxFastAttempts int
fastDelay time.Duration
slowDelay time.Duration
}
var _ RateLimiter = &ItemFastSlowRateLimiter{}
func NewItemFastSlowRateLimiter(fastDelay, slowDelay time.Duration, maxFastAttempts int) RateLimiter {
return &ItemFastSlowRateLimiter{
failures: map[interface{}]int{},
fastDelay: fastDelay,
slowDelay: slowDelay,
maxFastAttempts: maxFastAttempts,
}
}
func (r *ItemFastSlowRateLimiter) When(item interface{}) time.Duration {
r.failuresLock.Lock()
defer r.failuresLock.Unlock()
r.failures[item] = r.failures[item] + 1 // +1
if r.failures[item] <= r.maxFastAttempts { // 小于等于maxFastAttempts执行快速延时
return r.fastDelay
}
return r.slowDelay // 不满足执行慢延时
}
func (r *ItemFastSlowRateLimiter) NumRequeues(item interface{}) int {
r.failuresLock.Lock()
defer r.failuresLock.Unlock()
return r.failures[item]
}
func (r *ItemFastSlowRateLimiter) Forget(item interface{}) {
r.failuresLock.Lock()
defer r.failuresLock.Unlock()
delete(r.failures, item)
}
|
计数器快慢算法是最简单的延迟算法。其原理是当重复item的个数小于maxFastAttempts执行快速时延,否则执行慢速时延。比如maxFastAttempts为3,fastDelay是10ms,slowDelay是5s。通过AddRateLimited添加4个重复元素,那么前三个元素延时10ms,第四个元素延迟5s。
MaxOfRateLimiter – 混合限流算法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
| type MaxOfRateLimiter struct {
limiters []RateLimiter
}
func (r *MaxOfRateLimiter) When(item interface{}) time.Duration {
ret := time.Duration(0)
for _, limiter := range r.limiters {
curr := limiter.When(item)
if curr > ret {
ret = curr
}
}
return ret
}
func NewMaxOfRateLimiter(limiters ...RateLimiter) RateLimiter {
return &MaxOfRateLimiter{limiters: limiters}
}
func (r *MaxOfRateLimiter) NumRequeues(item interface{}) int {
ret := 0
for _, limiter := range r.limiters {
curr := limiter.NumRequeues(item)
if curr > ret {
ret = curr
}
}
return ret
}
func (r *MaxOfRateLimiter) Forget(item interface{}) {
for _, limiter := range r.limiters {
limiter.Forget(item)
}
}
|
在DefaultControllerRateLimiter中初始化了混合模式,包含了BucketRatelimiter 及ItemExponentialFailureRateLimiter
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| func DefaultControllerRateLimiter() RateLimiter {
return NewMaxOfRateLimiter(
NewItemExponentialFailureRateLimiter(5*time.Millisecond, 1000*time.Second),
// 10 qps, 100 bucket size. This is only for retry speed and its only the overall factor (not per item)
&BucketRateLimiter{Limiter: rate.NewLimiter(rate.Limit(10), 100)},
)
}
|
混合模式取的是两种模式的最大的延迟时间,最大的重新入列次数。按照上面的配置,一次前100个元素默认延迟10ms,如果有重复元素按指数退避计算延时时间,超过100个元素取令牌桶算法与指数退避算法的最大值。




